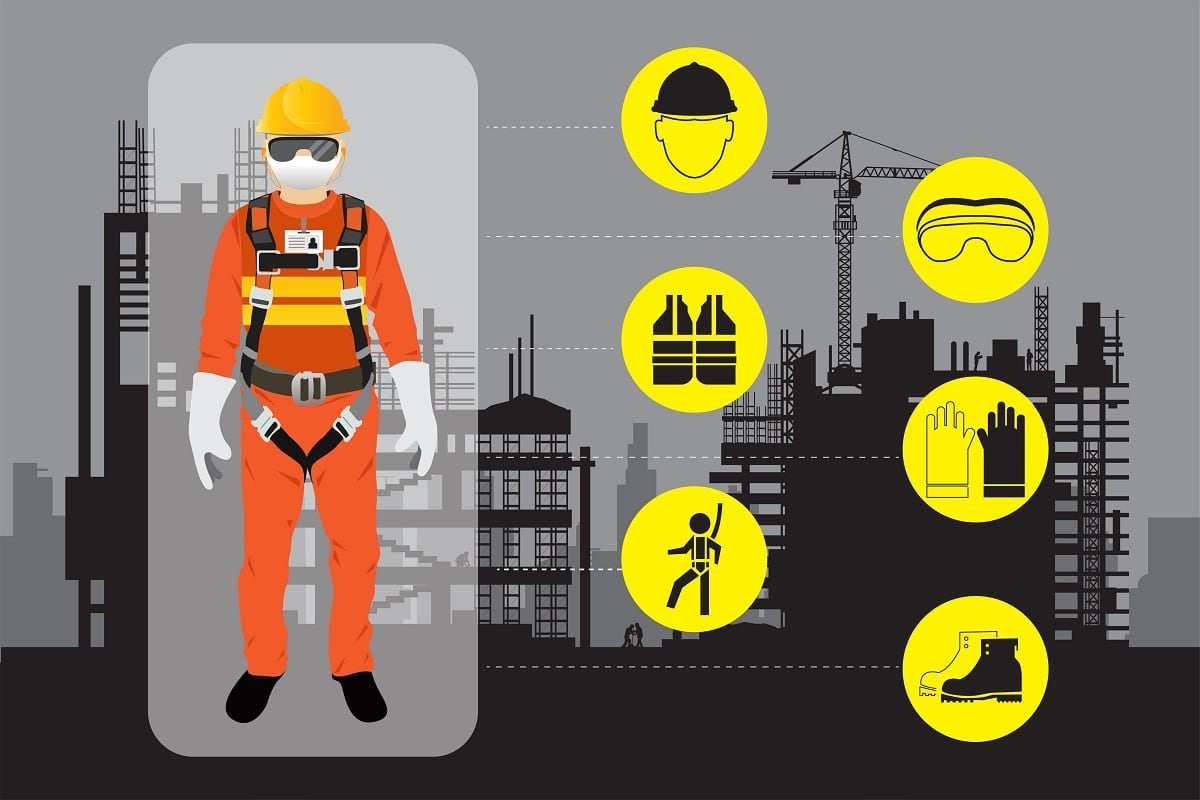
Who we are
OSHA SAFETY TRAINING CENTER was established in 2022 with the purpose of operation business regarding the Safety Training, Safety Auditing Safety Inspection, Safety Consultation and Safety Compliance “ISO” to any companies interested.

Work at Height
Working at height remains one of the biggest causes of fatalities and major injuries. Common cases include falls from roofs, ladders, and through fragile surfaces.

Scaffold Safety
Scaffolding safety is a combination of practices and safety procedures that enforces proper and safe use of scaffoldings. It involves a set of preemptive actions in building, inspecting, using, and tagging scaffolds.

First Aid & Basic Life Support
Basic Life Support (BLS) course provides healthcare providers and public safety professionals the knowledge and skills necessary to respond to breathing and cardiac emergencies in adult, child and infant patients. First Aid teaches students to recognize and care for a variety of first aid emergencies such as burns, cuts, scrapes, sudden illnesses, head, neck, back injuries, heat and cold emergencies.
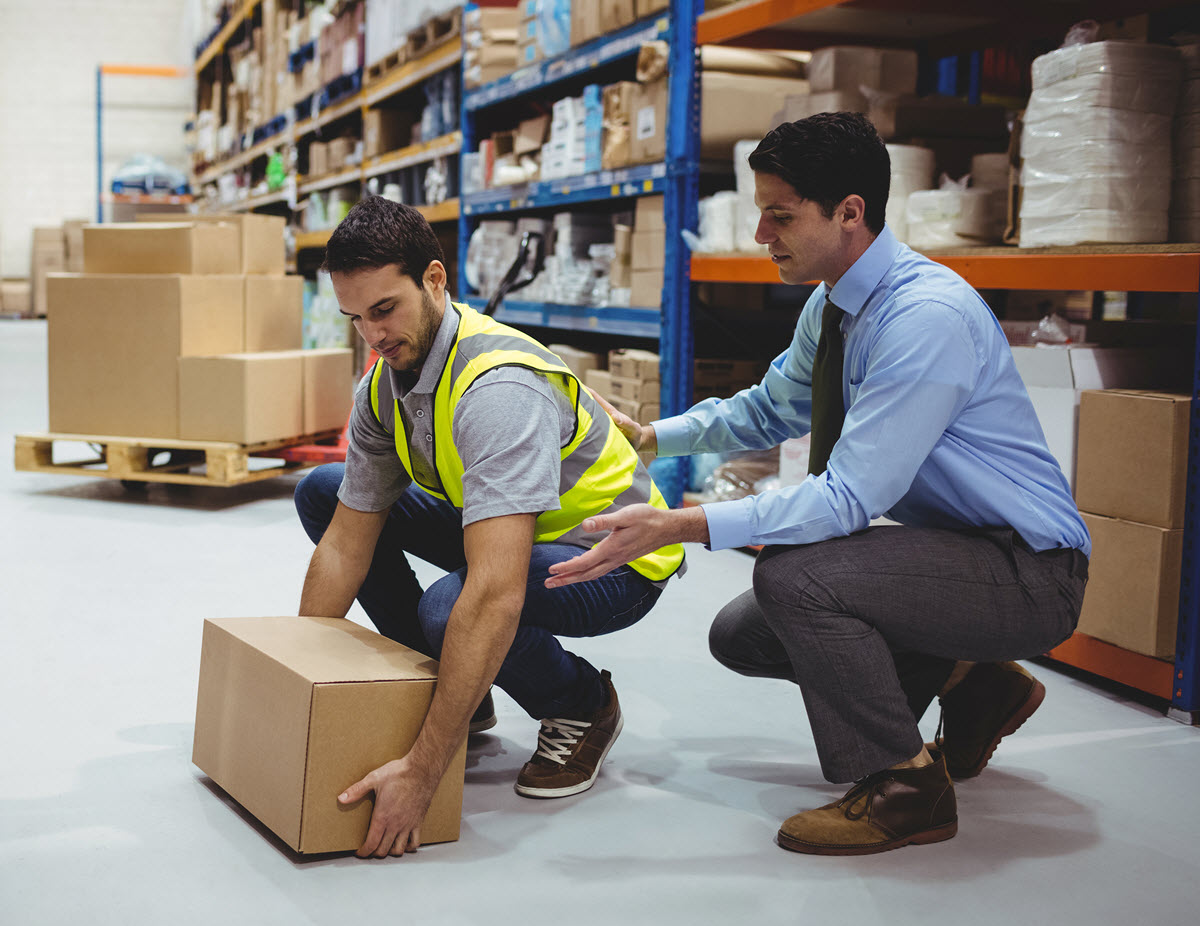

Ergonomics at workplace
is the science of designing the workplace, keeping in mind the capabilities and limitations of the worker. Poor worksite design leads to fatigued, frustrated and hurting workers. This rarely leads to the most productive worker. More likely, it leads to a painful and costly injury, lower productivity and poor product quality.
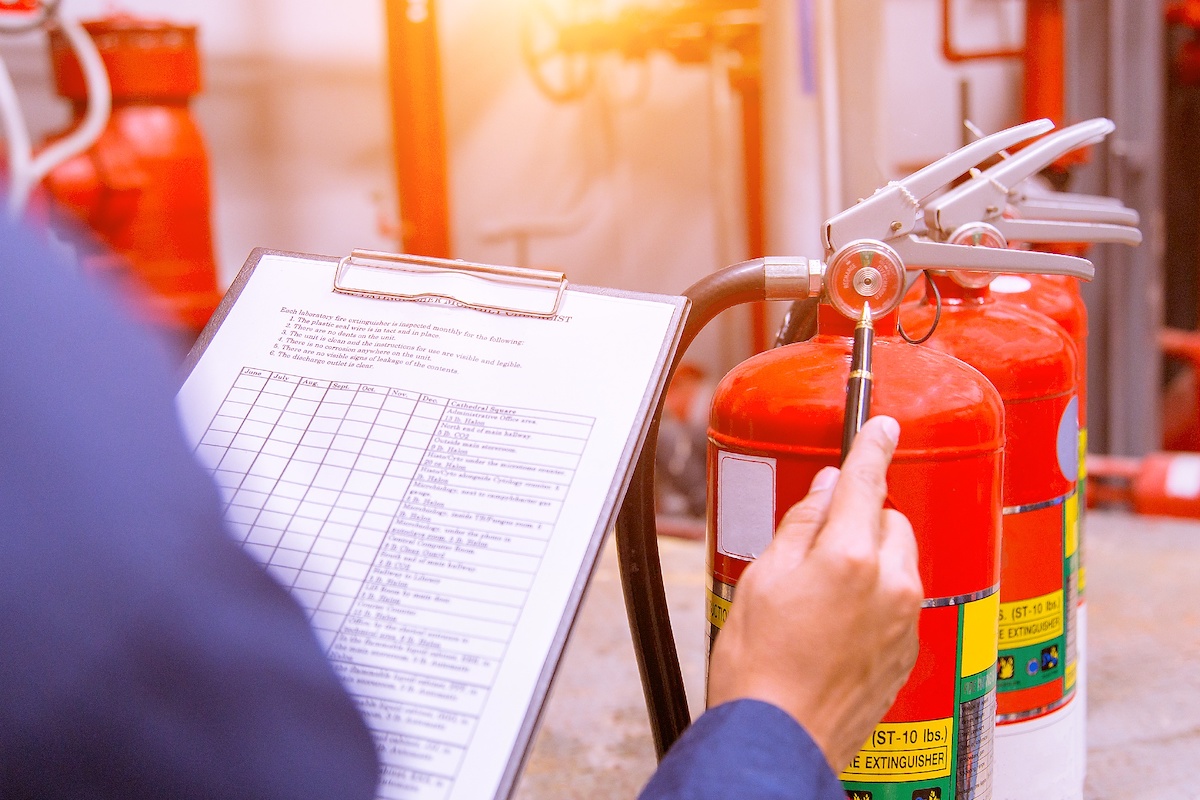

Fire safety & Fire fighting
Fire safety is a set of practices intended to reduce destruction caused by fire. Fire safety measures include those that are intended to prevent the ignition of an uncontrolled fire and those that are used to limit the spread and impact of a fire. Fire safety measures include those that are planned during the construction of a building or implemented in structures that are already standing and those that are taught to occupants of the building.
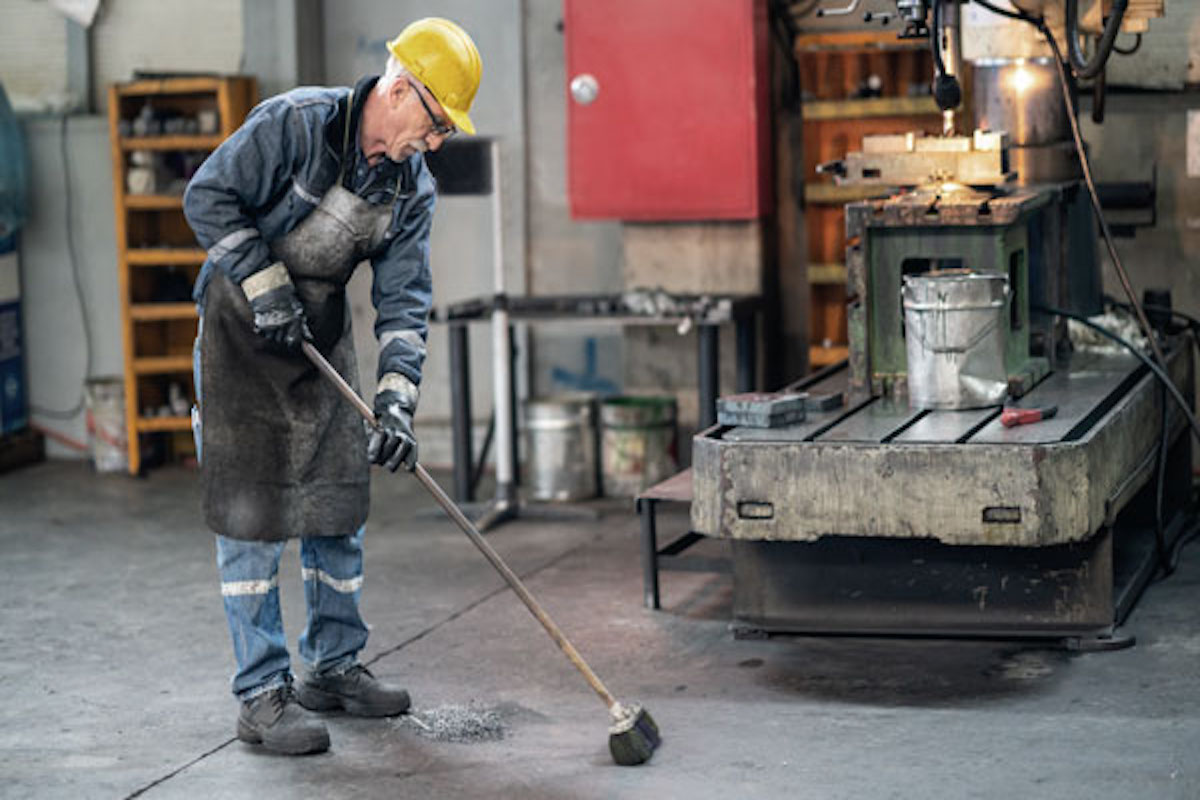

Housekeeping & 5S
Good housekeeping & 5S involves the principle of waste elimination through workplace organization. 5S was derived from the Japanese words seiri, seiton, seiso, seiketsu, and shitsuke. In English, they can be roughly translated as sort, set in order, clean, standardize, and sustain.
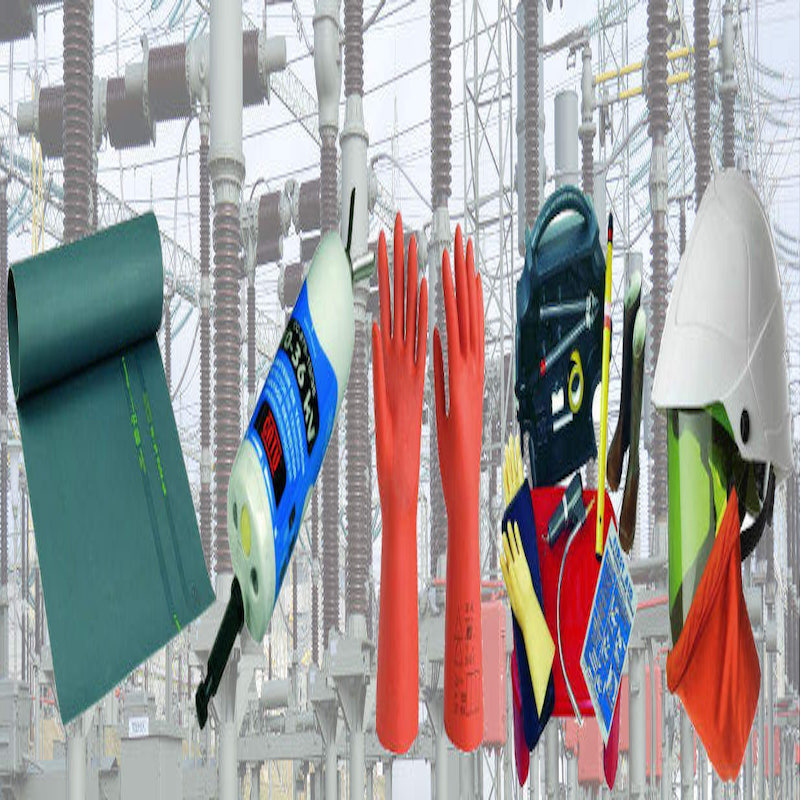

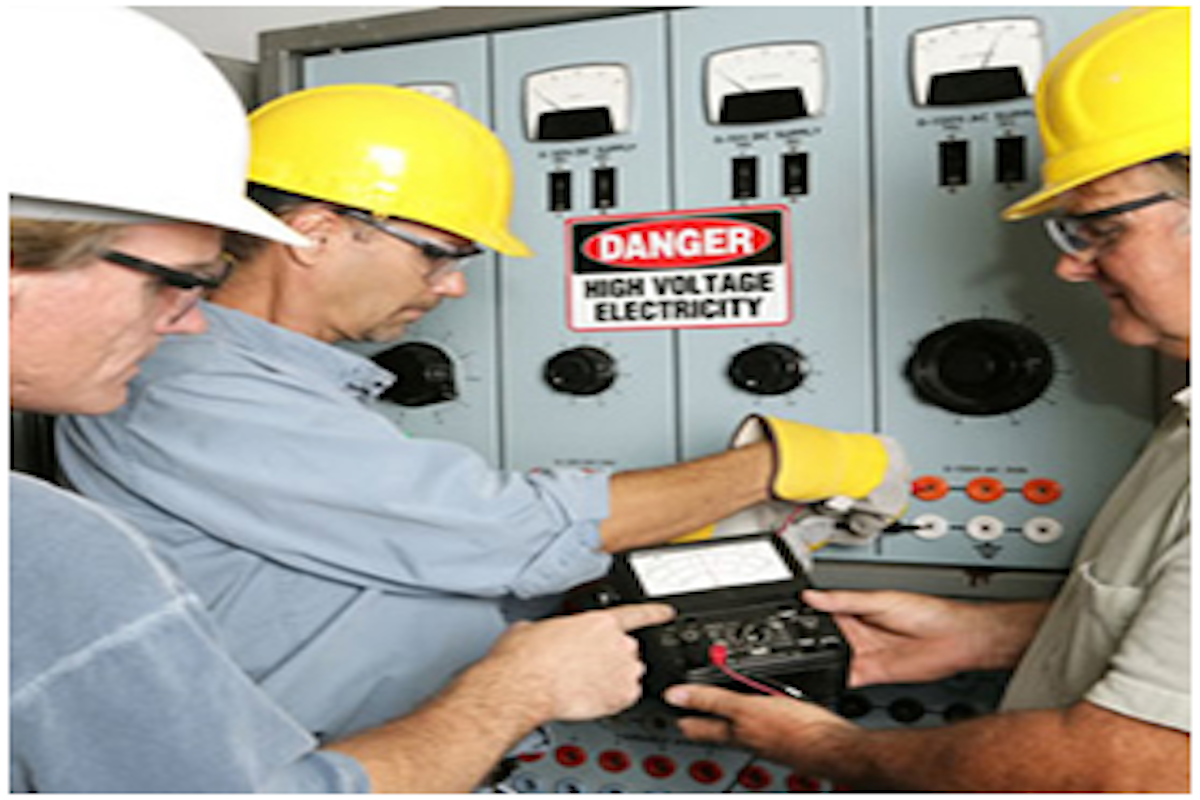
Electrical Safety
Electricity can kill or severely injure people and cause damage to property. However, employers can take simple precautions when working with or near electricity and electrical equipment to significantly reduce the risk of injury to themselves, their workers and others around them. This section provides a summary of those precautions.

Manual material Handling
Here's a list for safely lifting and moving materials: Maintain the correct posture: avoid bending over and keep lifts close to the body. Lift in a careful, deliberate manner and avoid any sudden lift movements. Never lift materials from a sitting position, or twist to pick up a heavy object.
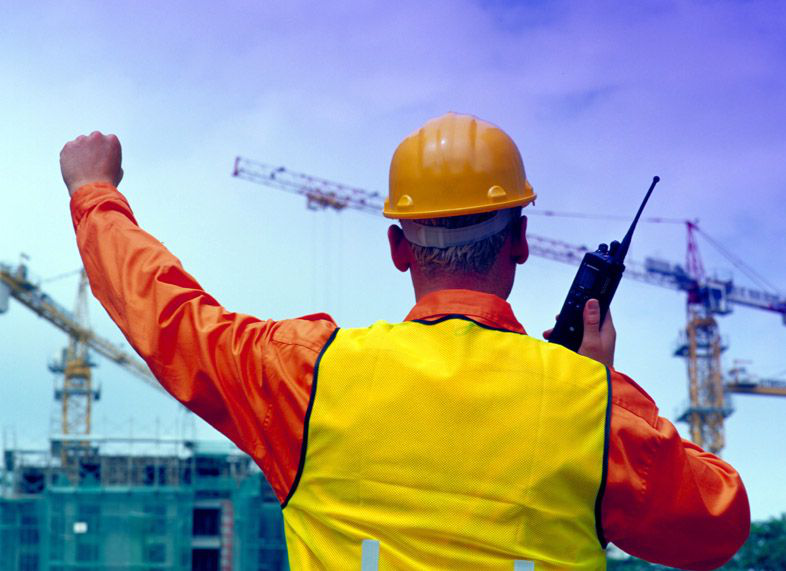

Hand Signal for Crane operations
Cranes are the most effective way to move heavy loads on a construction site, and proper use of crane hand signals is a vital part of safe operation
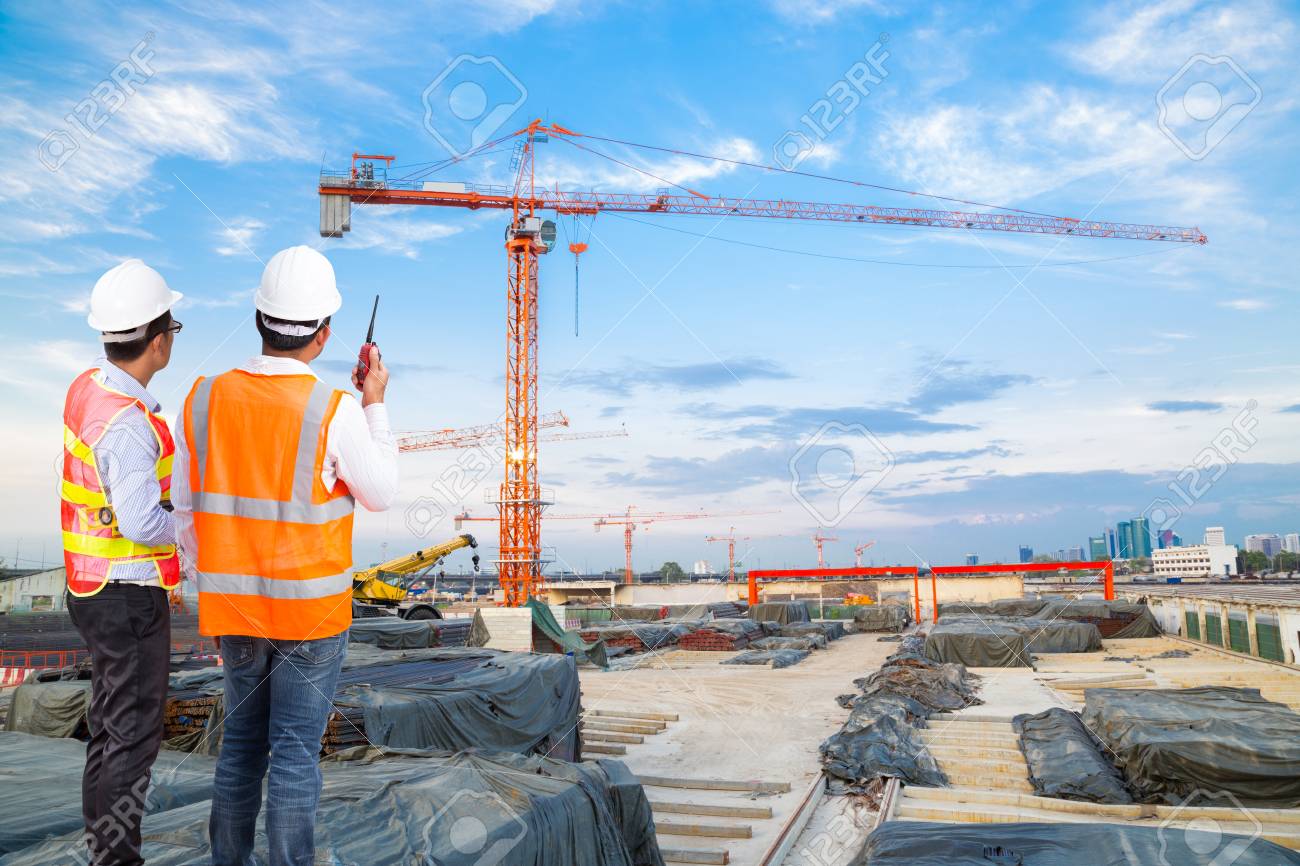

Construction Safety
Is an aspect of construction-related activities concerned with protecting construction site workers and others from death, injury, disease or other health-related risks. Construction is an often hazardous, predominantly land-based activity where site workers may be exposed to various risks, some of which remain unrecognized. Site risks can include working at height, moving machinery (vehicles, cranes, etc.) and materials, power tools and electrical equipment, hazardous substances, plus the effects of excessive noise, dust and vibration. The leading causes of construction site fatalities are falls, electrocutions, crush injuries, and caught-between injuries.

Lone working
Lone workers are those who work by themselves without close or direct supervision. Anybody who works alone, including contractors, self-employed people and employee, is classed as a lone worker.

Hazard Identification and Risk Analysis (HIRA)
One of the "root causes" of workplace injuries, illnesses, and incidents is the failure to identify or recognize hazards that are present, or that could have been anticipated. A critical element of any effective safety and health program is a proactive, ongoing process to identify and analysis such hazards.
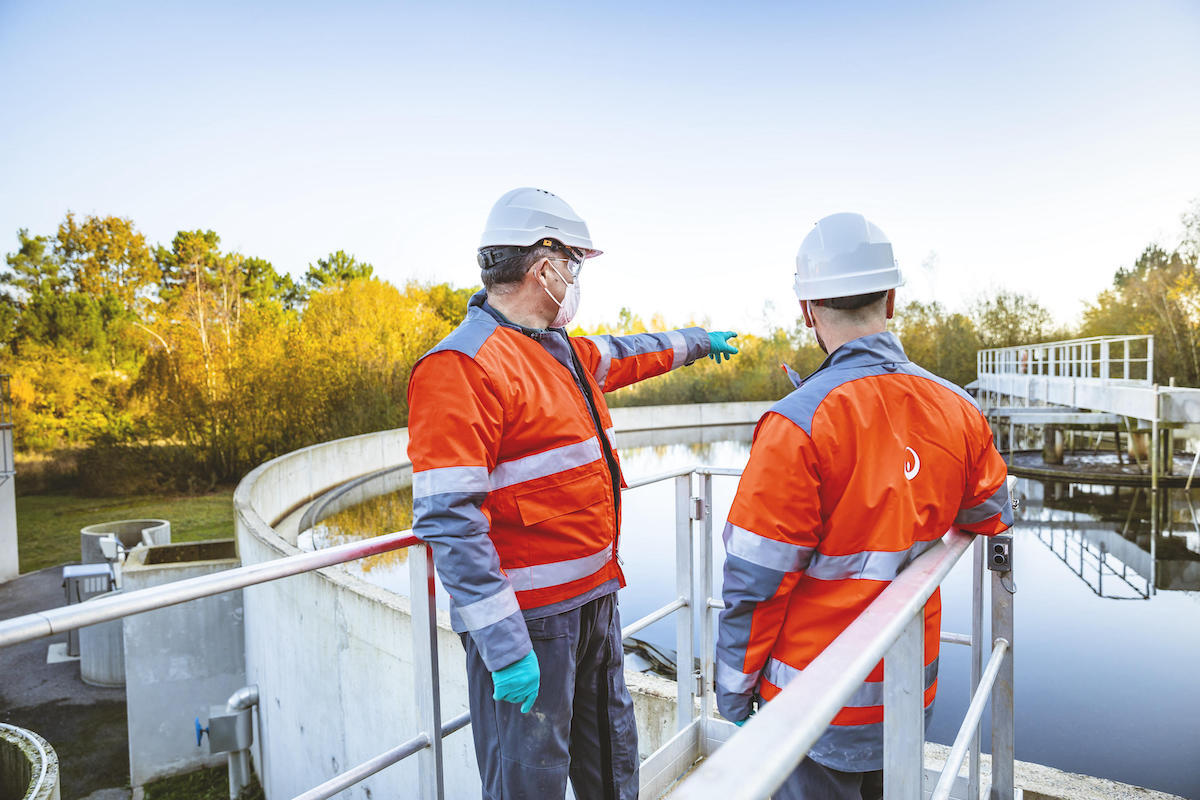

Industrial & Waste water management
Industrial wastewater treatment covers the mechanisms and processes used to treat waters that have been contaminated in some way by anthropogenic industrial or commercial activities prior to its release into the environment or its re-use. Most industries produce some wet waste although recent trends in the developed world have been to minimise such production or recycle such waste within the production process. However, many industries remain dependent on processes that produce wastewaters.

LOTO training
Lock Out Tag Out (LOTO) is a safety procedure to ensure that the Hazardous Energy Sources are "isolated" before work begins on the equipment in question. Lock Out Tag Out (LOTO) protects employees from physical harm or a fatal injury from any hazardous energy while servicing or performing maintenance activities.

Hazardous Area Classification (HAC)
Hazardous area classification is a technique for assessing the probability of formation of a flammable atmosphere and its likely duration.
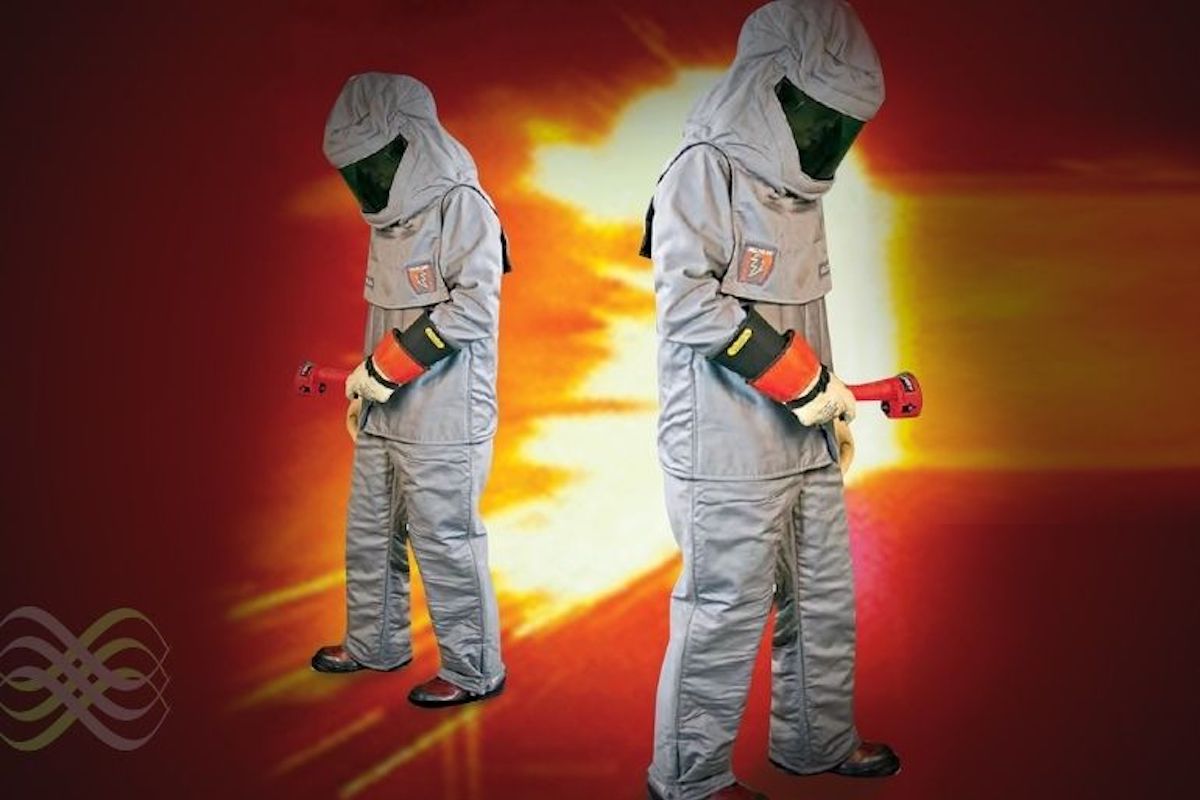

Arc Flash
An arc flash is the light and heat produced as part of an arc fault, a type of electrical explosion or discharge that results from a connection through air to ground or another voltage phase in an electrical system. Arc flash is distinctly different from the arc blast, which is the supersonic shockwave produced when the uncontrolled arc vaporizes the metal conductors.
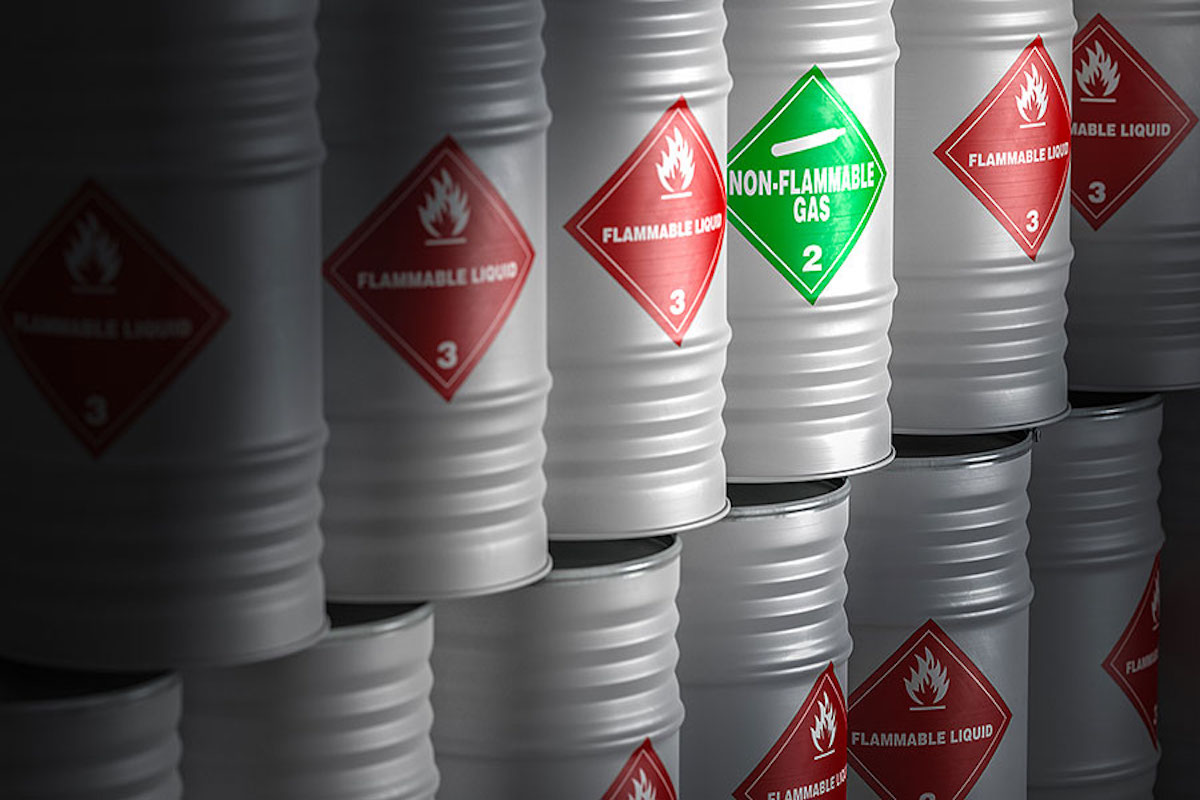

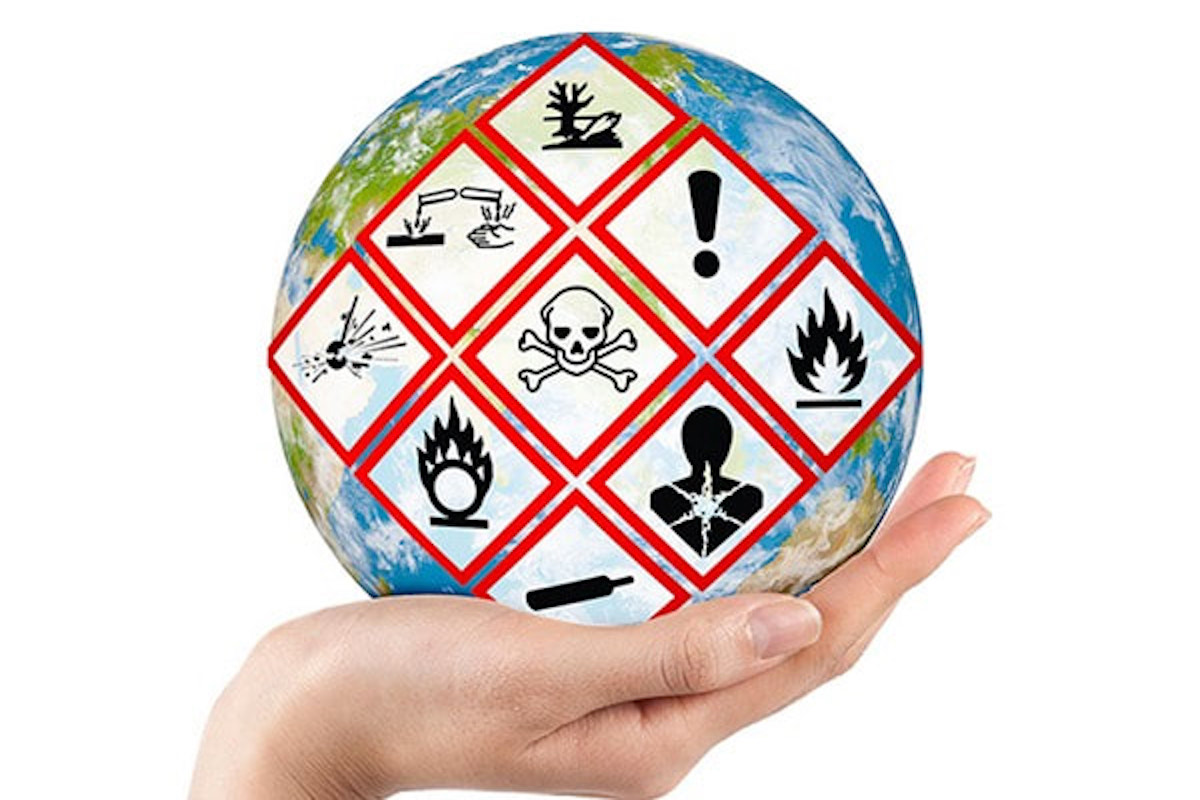
Hazard Communication
The Hazard Communication (also known as HazCom) is to protect people from injuries and illnesses associated with using hazardous chemicals in the workplace.
Emergency Action and Fire Prevention Plans
This section contains general emergency response procedures to be followed in the absence of department- or facility-specific procedures. The supervisor or person responsible for the area where an emergency occurs is responsible for investigating all emergency incidents and reporting them to Environmental Health and Safety.
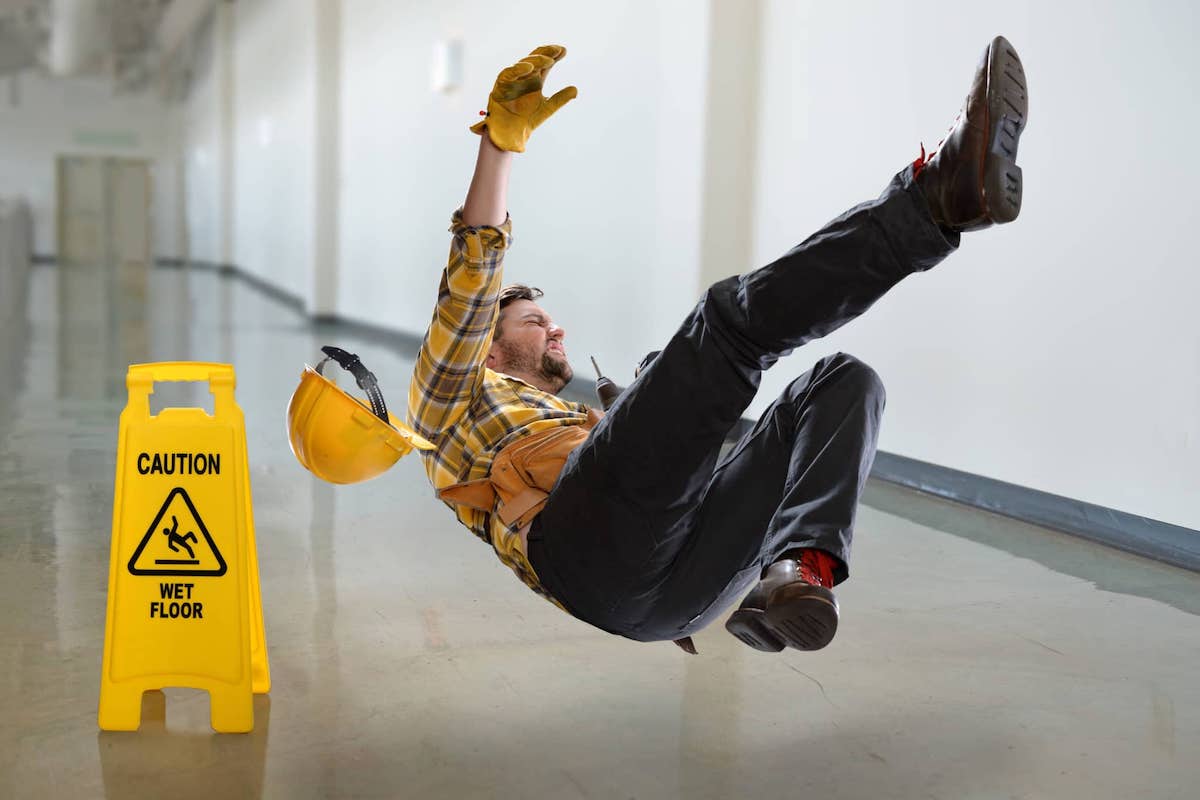

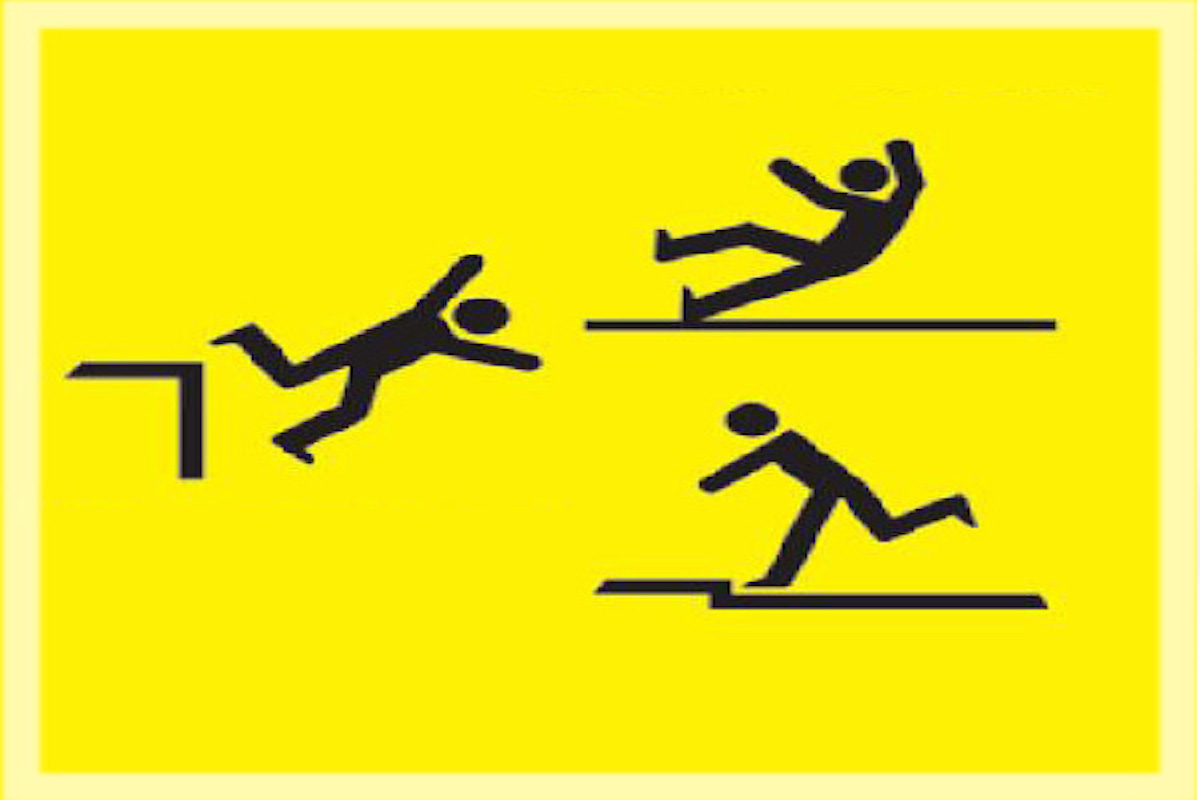
Walking - Working Surfaces and Fall Protection
General industry standards on walking-working surfaces to prevent and reduce workplace slips, trips, and falls, as well as other injuries and fatalities associated with walking-working surface hazards.

Driver Safety
Safety is something that drivers should keep in mind at all times. After all, when you are operating a motorized vehicle, you have a responsibility to do your part to keep the roadways safe for yourself, other drivers, passengers, and others who may be affected by traffic accidents.

Job Hazard Analysis - JHA
Job hazard analysis (JHA) identifies and analyzes hazards associated with the performance of various individual job tasks with the goal to make each worker as safe as possible.

Workplace Hygiene and Illness Prevention
Healthy Habits to Help Prevent Sickness Routinely clean frequently touched objects and surfaces, including doorknobs, keyboards, and phones, to help remove germs. Make sure your workplace has an adequate supply of tissues, soap, paper towels, alcohol-based hand rubs, and disposable wipes.

Physical Health Hazard in Construction
Physical hazards are different types of energy which may be hazardous to construction workers. They include noise, vibration, temperature extremes, and radiation.
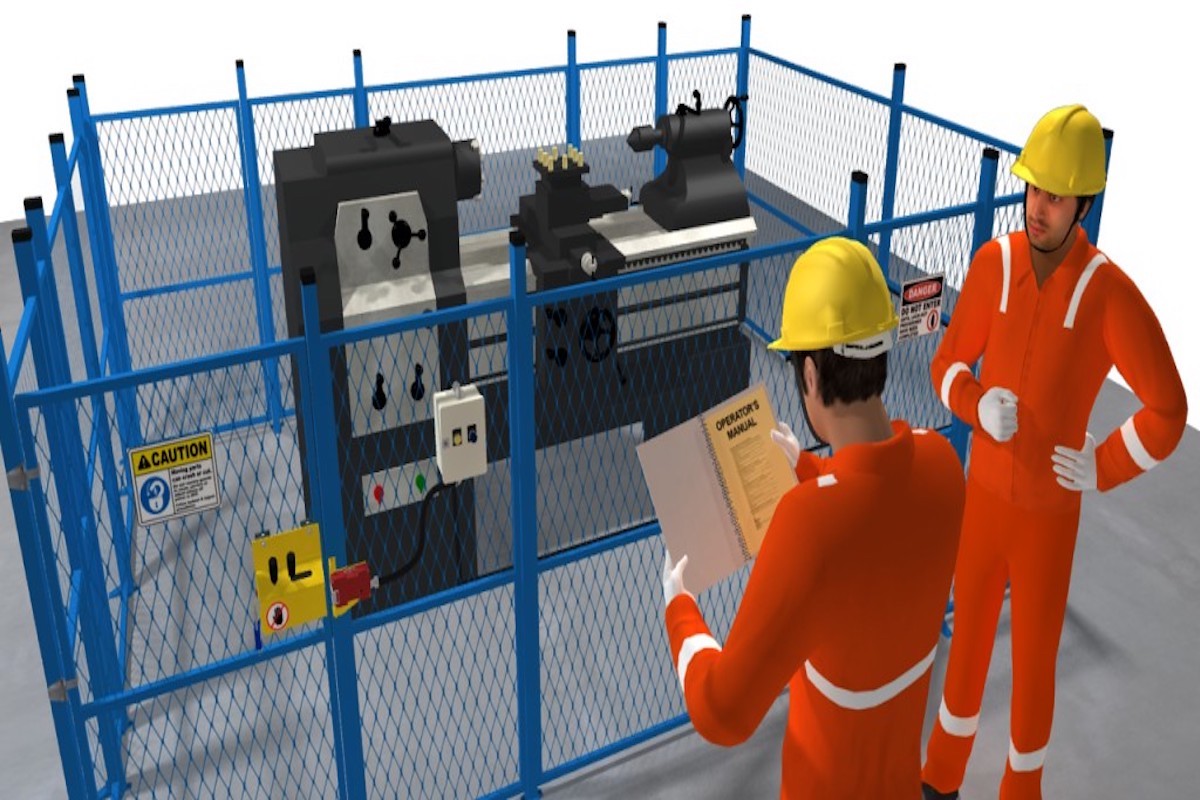

Machine Safeguarding
The machine guarding is to protect the machine operator and other employees in the work area from hazards created during the machine's normal operation. This would include hazards of concern such as: ingoing nip points, rotating parts, reciprocating, transversing, and/or flying chips & sparks. Any machine part, function, or process that might cause injury must be safeguarded. When the operation of a machine or accidental contact with it could injure the operator or others in the vicinity, the hazards must be either controlled or eliminated.
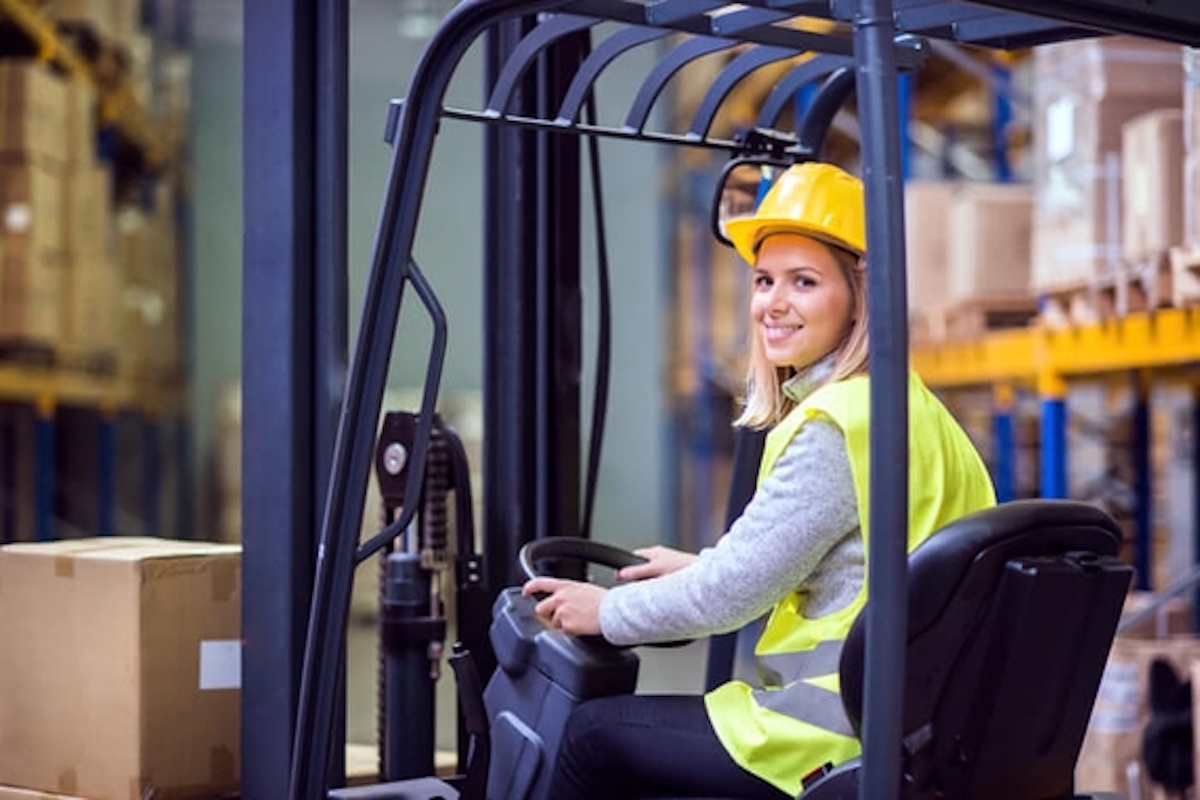

Forklift Safety
Forklifts are extremely useful workplace vehicles, as long as they are used safely and appropriately by operators who are appropriately trained and competent to use them. Forklifts can be dangerous. Many workplace accidents involve people being hit or run over by forklift trucks (typically when the forklift is reversing) because the driver did not see them. Owing to their size and weight, injuries resulting from forklifts are generally very serious. Accidents involving them are often caused by poor supervision and a lack of training.
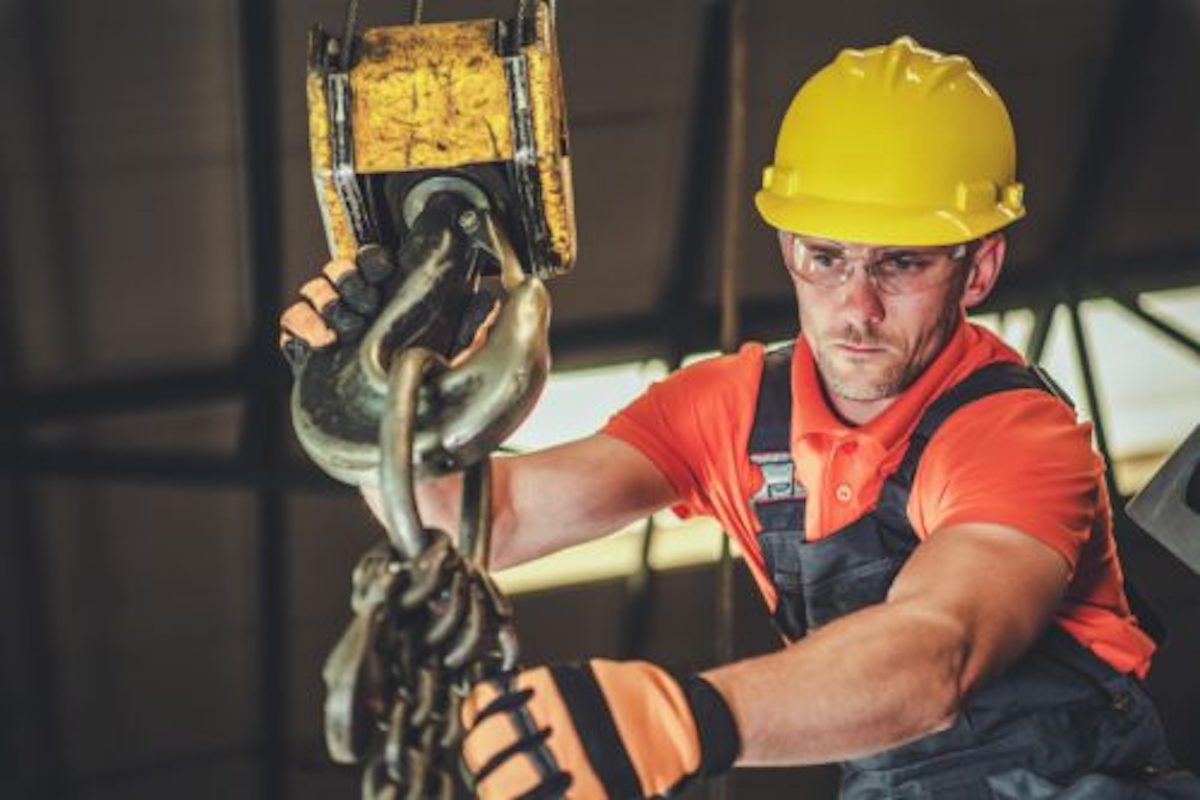

Crane Safety
Manufacturers, shipyard workers, and construction workers depend on industrial lifting devices to move large, heavy objects. While lifting devices like derricks, hoists, and cranes improve productivity and make work easier, they require special attention when it comes to safety.
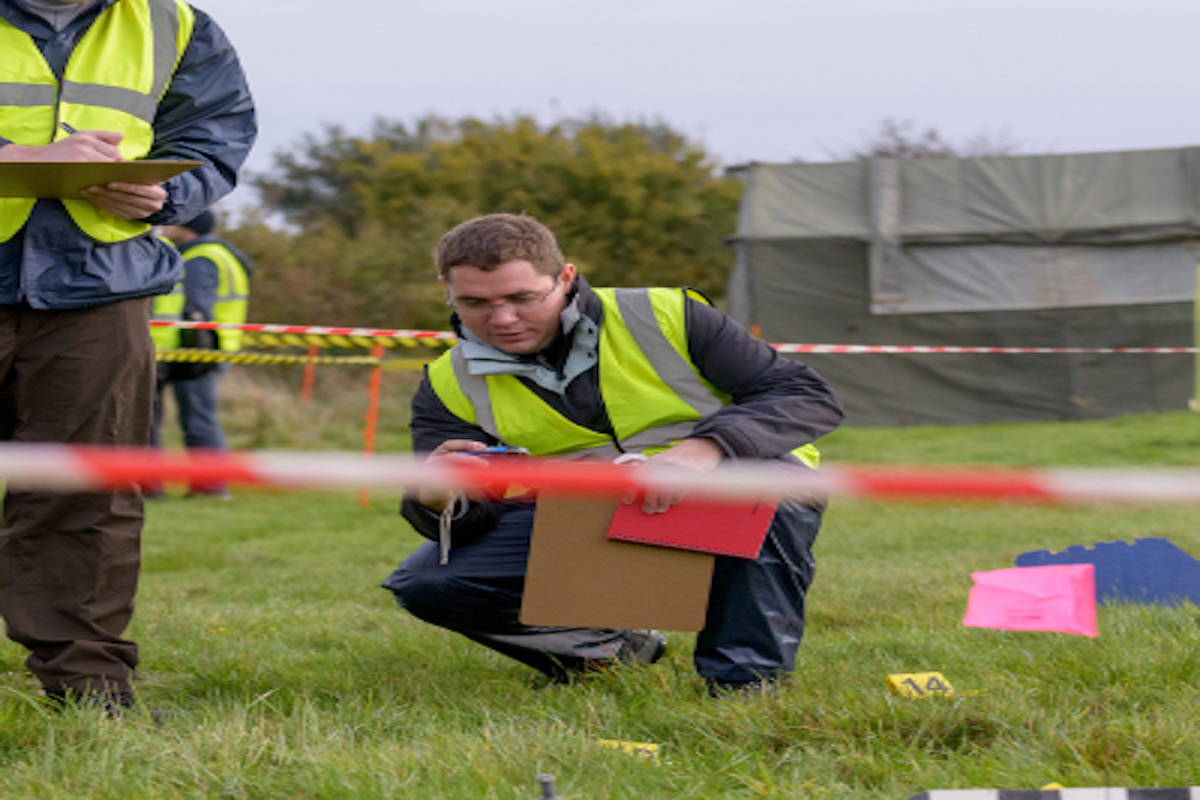

Accident Investigation
The failure of people, equipment, supplies, or surroundings to behave or react as expected cause most of the accidents. Accident investigations determine how and why these failures occur. By using the information gained through an investigation, a similar or perhaps more disastrous accident may be prevented. Conduct accident investigations with accident prevention in mind. Investigations are NOT to place blame.

School Safety Exterior Facilities
Poetatles as they can lead to chronic problems, such as the following: exposing students and teachers to mold and mildew poor ventilation potential for dangerous gases from cheap or sub-standard building materials Experts say outdoor air should be supplied on a continuous basis when students and/or teachers are in the portable classroom to improve the ventilation. If students or teachers experience eye or respiratory irritation, neurologic symptoms or difficulty concentrating while in the portable classrooms, they should immediately reduce exposure and get medical help. Poor lighting, extreme temperatures and noisy heating, and air conditioning can compromise the learning experience in portables. The structures often are placed in soggy fields or parking lots, near noise and vehicle exhaust.

School Safety Crisis Planning
Schools are well-organized systems that function with great efficiency under normal conditions. During a crisis, however, schools face unusual demands. While maintaining day-to-day operations, they must adapt to unexpected and unpredictable influences. Both school staff members and students will be personally affected by the crisis. Therefore, at the time of a crisis it is very difficult for a school to organize an effective crisis intervention response and still maintain the required long-range perspective. Schools may underestimate the full impact of the crisis or feel overwhelmed by the extent and magnitude of it. For schools to effectively address the many issues that typically arise during a crisis, a preplanned, systematic organizational model to direct decisions is essential. To be effective, a school's crisis response model must anticipate the results of a crisis and identify the ways it will affect individuals and the community. This includes identifying and preparing for the typical reactions of young people of all ages. In addition, the model must identify and plan how to use the broad range of skills and knowledge represented by those on the school crisis response team, including those of collaborating professions. Finally, the crisis response model must anticipate the future needs of the school population and develop plans to meet those needs.

Occupational Safety and Health
Occupational safety and health (OSH) or occupational health and safety (OHS), also known simply as occupational health or occupational safety, is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the safety, health, and welfare of people at work (i.e. in an occupation). These terms also refer to the goals of this field, so their use in the sense of this article was originally an abbreviation of occupational safety and health program/department etc. OSH is related to the fields of occupational medicine and occupational hygiene.
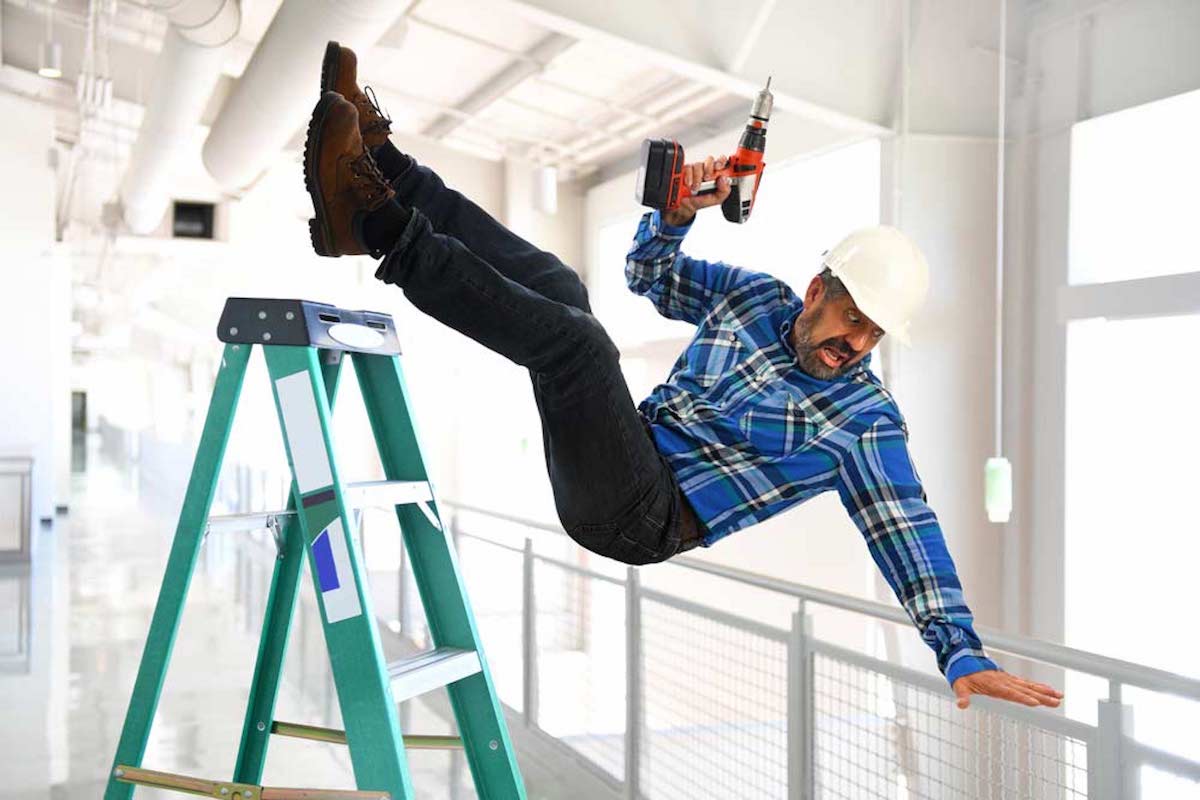

Stairway and Ladder Safety
Stairways and ladders are a major source of injuries and fatalities among construction workers due to falls from stairways and ladders used in construction.
WHYCHOOSE OSHA SAFETY?
Scope of Business Administration System
The quality manual of OSHA SAFETY is used as guideline for the whole organization, covering the process of distribution and performing to be satisfied by the client and or main contractors.
Quality Management System Policy
OSHA SAFETY has quality policy for all staff to know, we are committed to work in accordance with company quality management system following “Committed provided with the best of
quality on time to ensure the client and or main contractor satisfaction”
WANT TO
certify ISO & SAFETY WITH US?
CONTACT US
+855 (0) 77 738 821
+855 (0) 88 866 6787
Info@globalisosafety.com
oshasafetyt@gmail.com
ADDRESS:Phnom Penh, Cambodia.